Bitcoin’s price is soaring, and eyes are now on the upcoming “halving” event and its potential influence. Some believe it’s a critical factor driving value due to increased scarcity, while others see it as a technical tweak inflated by speculation. Let’s break down what it is and its impact.
What is the Halving?
Built into Bitcoin’s core blockchain technology, the halving reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are created. Designed with a capped supply of 21 million, Bitcoin’s creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, programmed this mechanism to slow down new coin issuance.
Currently, around 19 million bitcoins are in circulation.
How Does it Work?
Blockchain technology relies on “blocks” containing information added to a chain through “mining.” Miners use computing power to solve complex puzzles to build the chain and earn rewards in new bitcoins.
During a halving, the reward amount for miners gets cut in half, making mining less profitable and slowing down new bitcoin production.
When is it Happening?
While there’s no exact date, it’s expected for late April. The halving is programmed to occur every 210,000 blocks added to the chain, roughly every four years.
Impact on Price?
Scarcity is a key factor for some Bitcoin enthusiasts, believing it gives the cryptocurrency value. The logic is that with a lower supply, prices should rise as demand stays constant or increases.
However, others argue that any impact would already be reflected in the current price.
Additionally, the opaque nature of the crypto mining sector, with limited data on inventories and miner behavior, adds uncertainty. If miners sell their reserves, it could push prices down.
Understanding the reasons behind a cryptocurrency rally is difficult, especially with less transparency compared to traditional markets.
The recent surge is often attributed to the approval of Bitcoin ETFs by the SEC and expectations of central banks lowering interest rates.
In the speculative world of crypto, analyst explanations can snowball into self-fulfilling market narratives.
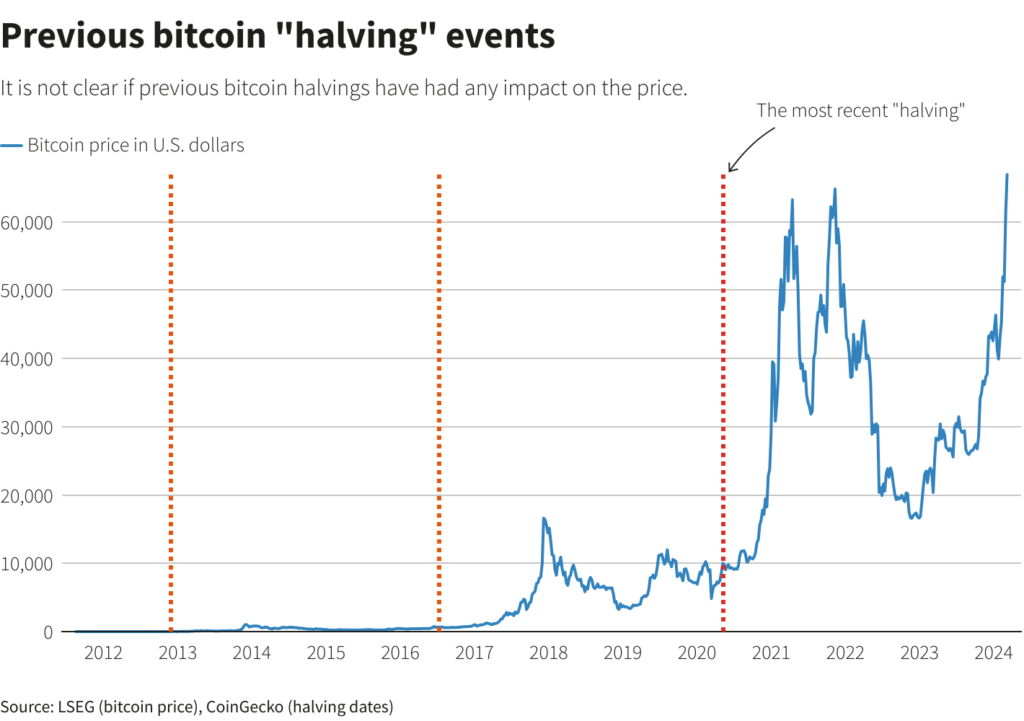
There’s no clear evidence that past halvings directly caused price increases. However, traders and miners analyze historical data to gain an edge.
While there was a price rise after the May 2020 halving, other factors like loose monetary policy and increased retail investor activity likely played a role.
Similarly, the 2016 halving saw a small initial rise followed by a price drop. Overall, isolating the halving’s impact is challenging, making future predictions difficult.
Regulatory bodies continue to warn about the speculative nature of the Bitcoin market, fueled by hype and fear of missing out (FOMO), posing risks to investors despite approving Bitcoin trading products.
Discover:

Cryptoassets:
The Innovative Investor’s Guide to Bitcoin and Beyond
$14.85 (35% off)
Cryptoassets represent the future of money and markets. This book is your guide to that future.

